MaaS Alliance and the World Resources Institute (WRI) have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for Strategic Partnership to support the Parties knowledge-sharing and collaboration on creating momentum and scalability for sustainable mobility services and the Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS). MaaS Alliance and the World Resources Institute are working together to promote public transport and shared mobility through a Mobility-as-a-Service solution.
The agreement will support science and evidence-based implementation and policy-making within this field to advance solutions to reduce carbon emissions, improve road safety, and increase equal opportunities. The collaboration focuses on the areas including knowledge-sharing on MaaS and future mobility development, promoting green and sustainable mobility in each Parties’ networks, development of MaaS guidance and framework that can be used locally, developing assessment tools and training, jointly hosting workshops and events for knowledge-sharing and engagement.
WRI China is leading a project, “100 MaaS Cities in China”, which is under the Reimaging Public Transport Initiative with the aim to revive and thrive public transport in Brazil, China, India, Mexico, and beyond. Under the MaaS project in China, WRI has been working with stakeholders to develop multiple research and engagement activities in the next 2-3 years (see the figure). The project aims to cultivate integrated and smart mobility systems that connect active transport (bike-sharing and walking) and ridesharing with public transport through MaaS solutions. MaaS services in China will be public transport and an active transport-dominated system. The project will seek to scale up to 100 Chinese cities through national-level promotions, making more people enjoy convenient, safe, healthy, and modern transit systems with net-zero emissions.
Figure 1: Activities of WRI’s MaaS project in China for the next two years
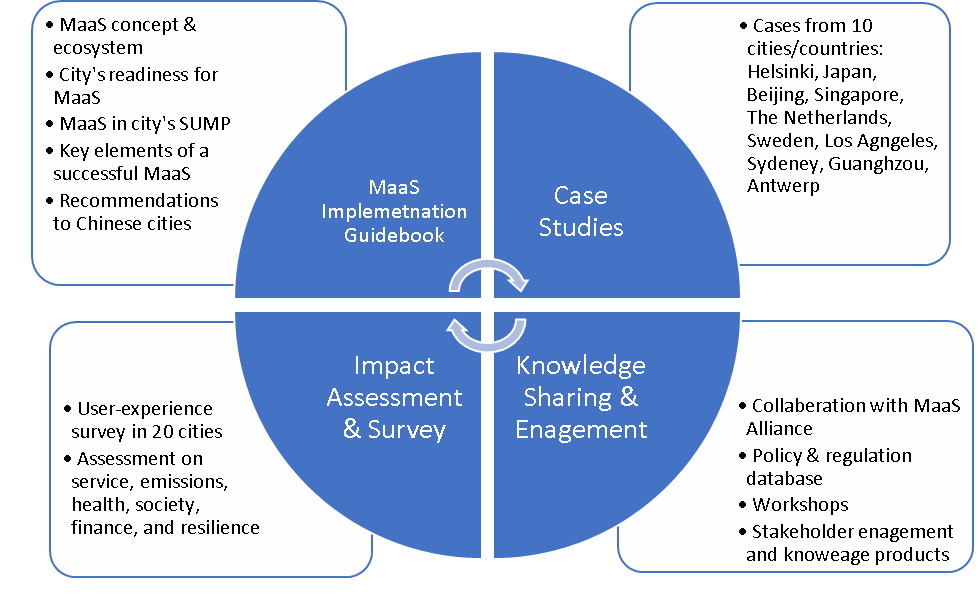
Source: WRI (2021)
China has a booming market of shared economy and shared mobility. By the end of 2020, the market transactions of all shared mobility services in China exceeded 227.6 billion CNY (35.8 billion US$), with total trips over 32.3 million person-times. Shared mobility services also generated significant employment opportunities. According to Didi Chuxing, China’s biggest TNC (transport network company) on ridesharing/ride-hailing and bike-sharing services, there were more than 1.5 million registered drivers in their platform by the first half of 2020, and additional 3 million flexible jobs by 2020.1
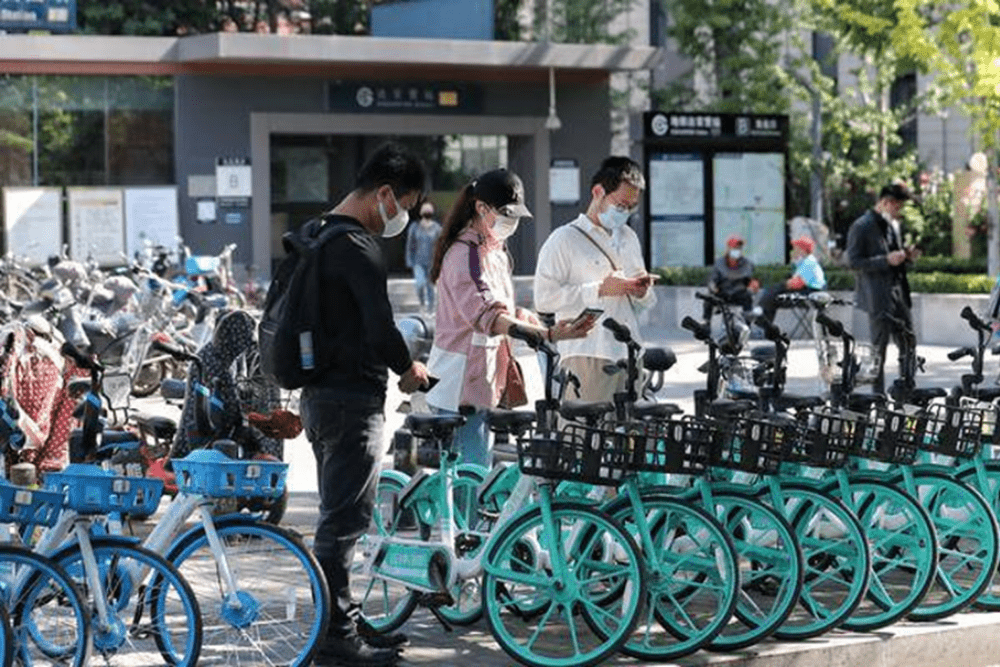
Dockless bike-sharing (DBS) and shared e-bike systems play an important role in urban mobility, especially in terms of providing first/last-mile solutions connecting to bus and metro stations. By the end of 2020, DBS has been operating in more than 360 Chinese cities with over 19 million bikes and 45.7 million daily orders.1 People tend to ride more after COVID-19, and more cities encourage a MaaS system with integration of public transport and bike-sharing services, such as Beijing, Guangzhou, and Shanghai. According to WRI’s study in 12 Chinese cities, more than 54% of DBS users used DBS to connect other modes, from which 91% of the linking trips were used to access public transport.2
Although there is a huge demand from both city government and citizens on an integrated and smart transport system, city decision-makers have limited knowledge of MaaS and the relevant action guide. The collaboration between MaaS Alliance and WRI will fill these gaps in China and beyond. And the international good practices and experience from MaaS Alliance can also help Chinese stakeholders to reach green mobility more sustainably.
****
WRI is a global non-profit organization that works with leaders in government, business and civil society to research, design, and carry out practical solutions that simultaneously improve people’s lives and ensure nature can thrive.
MaaS Alliance is a global public-private partnership creating the foundations for a common approach to MaaS, unlocking the economies of scale needed for successful implementation and take-up of MaaS in Europe and beyond. The main goal is to facilitate a single, open market and full deployment of MaaS services.
****
References:
1 CEPF; NCUT; CATARC. Annual Report on the Development of Shared Mobility in China |中国共享出行发展报告 (2020-2021). 2021 https://www.pishu.com.cn/skwx_ps/bookdetail?SiteID=14&ID=12470917 (accessed Nov 18, 2021).
2 Jiang H, Song S, Zou X, Lu L. How Dockless Bike-Sharing Changes Lives: An Analysis of Chinese Cities. 2020 DOI:10.46830/wrirpt.18.00124.



